Sharing helps us build more free tools
Kendall rank correlation is used to measure the correlation between two ordinal measures. Ordinal measures show the rank of something, e.g. placings in a race.
The heatmap below shows the Kendall rank correlation coefficients for columns in the mt cars data set.
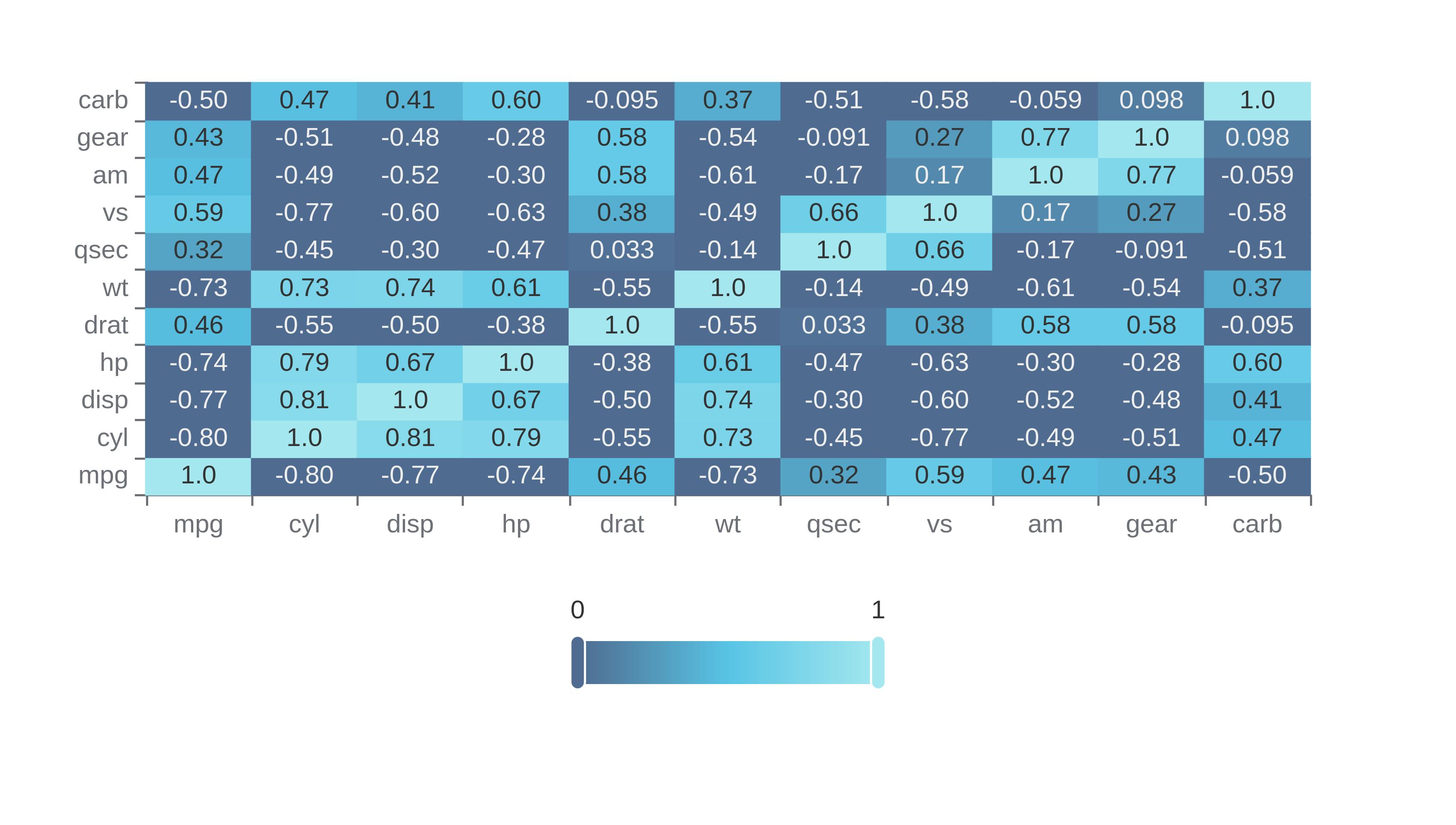
A Kendall Rank Coefficient close to 1 means that the two measures are highly similar and have a positive correlation. When one measure has a high rank then so does the other one.
A Kendall Rank Coefficient close to -1 means that the two measures are highly dissimilar and have a negative correlation. When one measure has a high rank then the other has a low rank.
A Kendall Rank Coefficient close to 0 means that there is no correlation between the two measures. The rank in one measure does not relate to the rank in the other measure.
When To Use Kendall Correlation
Kendall Correlation is useful for calculating the correlation between ordinal (aka ranked) measures. The correlation coefficients can be used to figure out if changes in one measure relate to changes in another measure.
The Kendall rank correlation coefficient is similar to the Spearman correlation coefficient. The Spearman coefficient calculator can be used to calculate Spearman coefficients. For rank correlation, it often does not matter whether the Kendall or Spearman correlation method is used.
How To Calculate Kendall Correlation
Upload your dataset
Click the dataset input at the top of the page. Or drag and drop your dataset into the input box.
View your Kendall Correlation
A heatmap with the Kendall Correlation of each column against each other column will appear on the screen
Download Kendall Correlation Heatmap
Click the download button on the heatmap to download an image of your Kendall Correlation